HTTPS refers to an updated form of HTTP web connection, with the S standing for secure. With internet use evolving from simple hobbies to important real life uses such as financial and medical uses, the need for encryption in websites has become increasingly important. The main purpose of HTTPS is to provide the secure and encrypted connection between users and websites as well as ensuring that users have privacy while using such websites. In order to circumvent the encryption and security provided by HTTPS, various ISPs, government entities, schools utilize a tool known as a Proxy Appliance which essentially decrypts and logs all material sent by the user of the browser as the user has to go through the Proxy Appliance to connect to the internet.
A MITM or a man in the middle attack is a term used for when an attacker is in the middle of a transfer of information between a user and an application. This is done in order to steal sensitive private information such as bank account information, medical information, login credentials, etc. This is usually done by intercepting then decrypting the transfer of information, through a variety of methods such as IP spoofing, ARP spoofing, HTTPS spoofing, SSL hijacking, etc. A hash is a complex mathematical algorithm which carefully processes all the information that it receives. A good hash is one that is efficient in processing information as well having the least collisions possible.
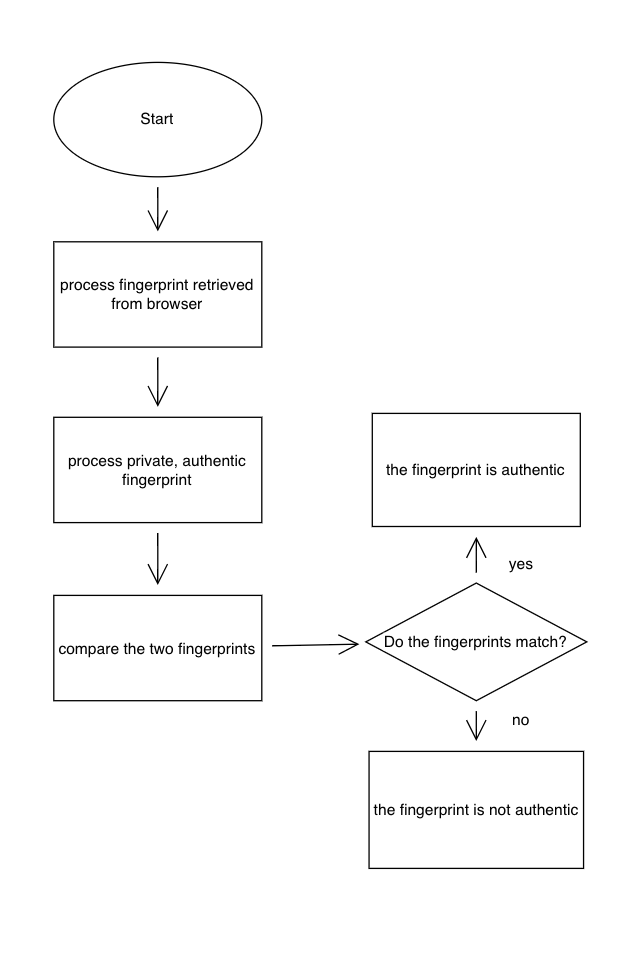
A CA also known as a Certificate Authority is an entity to whom web sites prove their identity to utilizing physical incorporation documentation. After proving its identity, certificate authorities will approve and sign the site’s security certificate. These certificates are used to prove the identities of websites and ensure secure connections. An SSL Interception can not be prevented however it can be reliably detected because it is not possible to spoof a security certificate. It can be easily detected by checking the website's original fingerprint and comparing it to the fingerprint found by the user, if they’re different then an SSL interception has occurred.
A false positive is a negative that was originally conceived to be a positive, and vice versa for a false negative. In the sense of Cybersecurity, it is when a threat is detected, when there is no threat, while a false-negative is when a threat is not detected but it is still present.
Steve Gibson, G. I. B. S. O. N. R. E. S. E. A. R. C. H. C. O. R. P. O. R. A. T. I. O. N. (n.d.). GRC : SSL TLS HTTPS web server certificate fingerprints. GRC | SSL TLS HTTPS Web Server Certificate Fingerprints.Retrieved August 25, 2022, from https://www.grc.com/fingerprints.htm#top
Imperva. (2019, December 29). What is MITM (man in the middle) attack. Imperva. Learning Center. Retrieved August 25, 2022, from https://www.imperva.com/learn/application-security/man-in-the-middle-attack-mitm/
Fichtner, E. (2022, March 8). Cybersecurity 101: What you need to know about false positives and false negatives. Datto. Retrieved August 25, 2022, from https://www.datto.com/blog/cybersecurity-101-what-you-need-to-know-about-false-positives-and-false-negatives#:~:text=What%20Are%20False%20Negatives%3F,ability%20to%20detect%20these%20attacks.